Ischemia without arteries obstruction is a heart disease which is gaining more attention nowadays. Especially since it is related to the female heart. Ischemia with no obstructive coronary arteries as it is called by physicians or in short INOCA (INOCA) is difficult to detect. Other names used for this type of heart problems are coronary microvascular dysfunction or coronary artery spasm. Both labels refer to a situation where insufficient blood can move through the very small arteries in the heart to supply the muscles with oxygen. In a very effective overview published by the American College of Cardiology the technical details of this disease and the way doctors have developed an approach for detection are described.
Ischemia without arteries obstruction happens more with female hearts than males. It is considered a major issue in early identification of ischemia within females. Males apparently have a higher tendency to have blocked arteries in the main vessels and this is much easier to detect.
In 2012 the Coronary Vasomotor Disorders International Study (COVADIS) study group was established and this team developed international standards for the diagnostic criteria of microvascular and vasospastic angina. These guidelines are now used in national and European guidelines. So when people show stable chest pain following these guidelines is currently the method applied both in the USA and Europe.
The guidelines offer two major options for action once microvascular artery problems are considered a feasible diagnostic option: Non-Invasive and Invasive diagnostic technologies.
Non Invasive diagnosis of Ischemia without arteries obstruction
Applying a non invasive approach is always easier for patients but there are some nuances. The guidelines suggest to use an approach which combines a person stopping to use caffeine for a period of 24-48 hours followed by adding chemical components which stimulate the level of blood in the organs. This is needed to register is the blood flow is altered since the arteries are too small to used the normal heart imaging techniques.
And within this approach physicians can choose between using a PET scan, Magnetic Reasonance (MRI) or Ultrasound (Echo).
Invasive diagnosis of Ischemia without arteries obstruction
If the non invasive approach still does not provide clear answers the next level is go measure within the body. Again the blood flow registration is the key target. For this purpose the guidelines suggest two technologies: a doppler wire which support an ultrasound based recording from within the arteries or a pressure-temperature sensor which also requires to be located inside the arteries. Naturally, an invasive approach takes even more time and requires a larger team of specialists.
The ECG as the next non-invasive solution
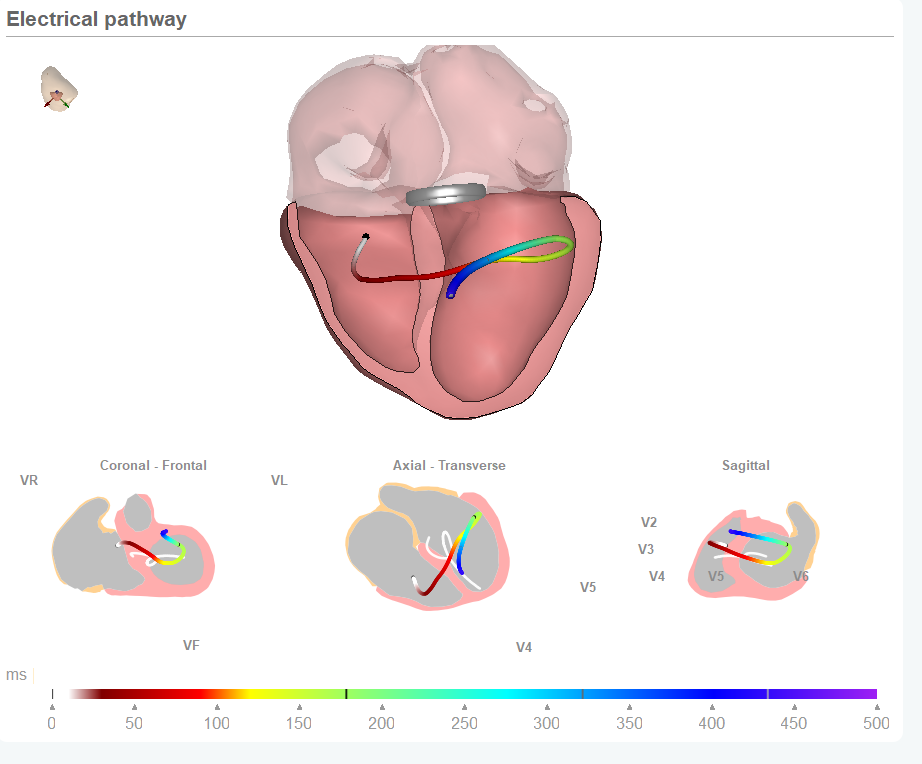
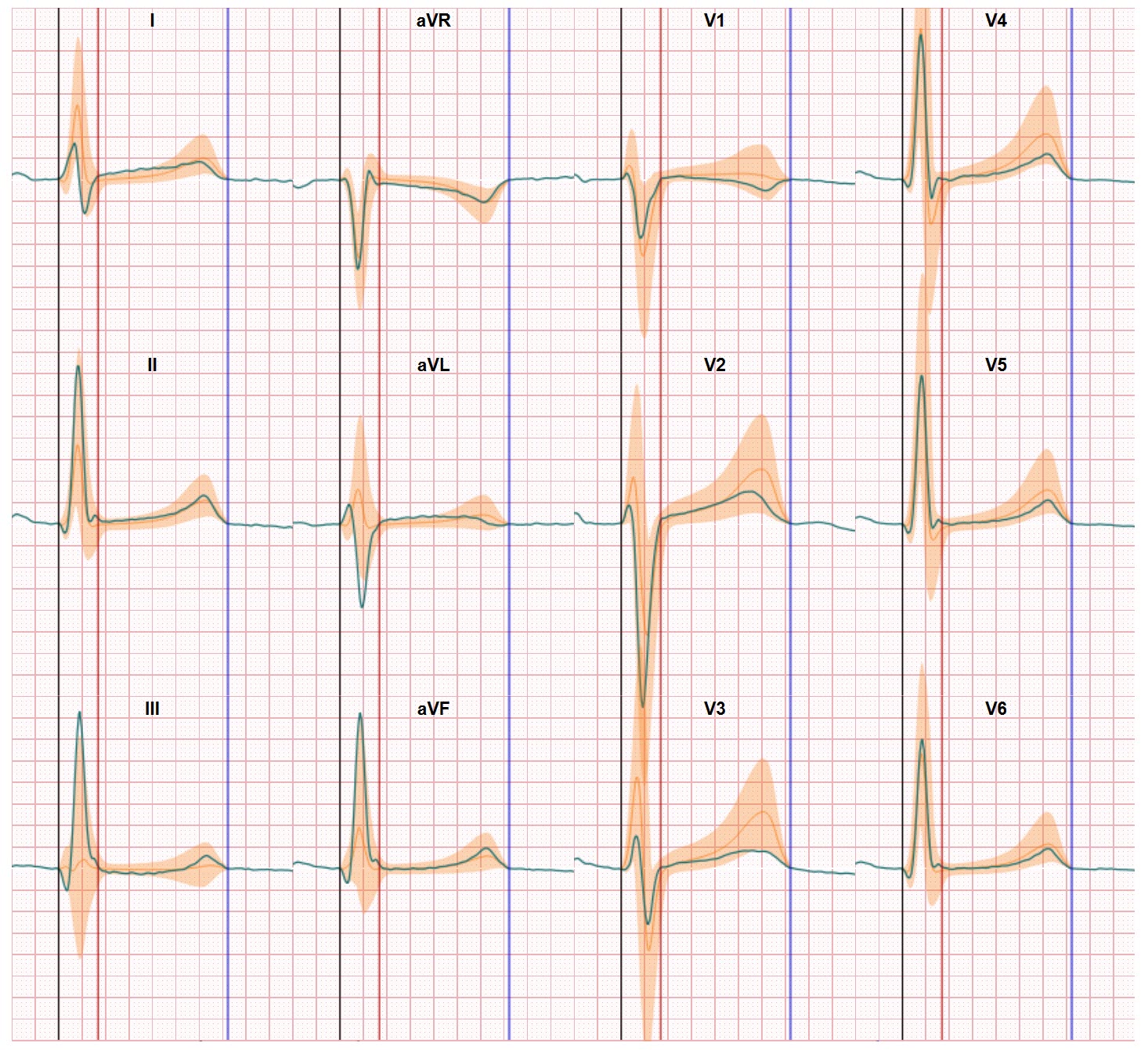
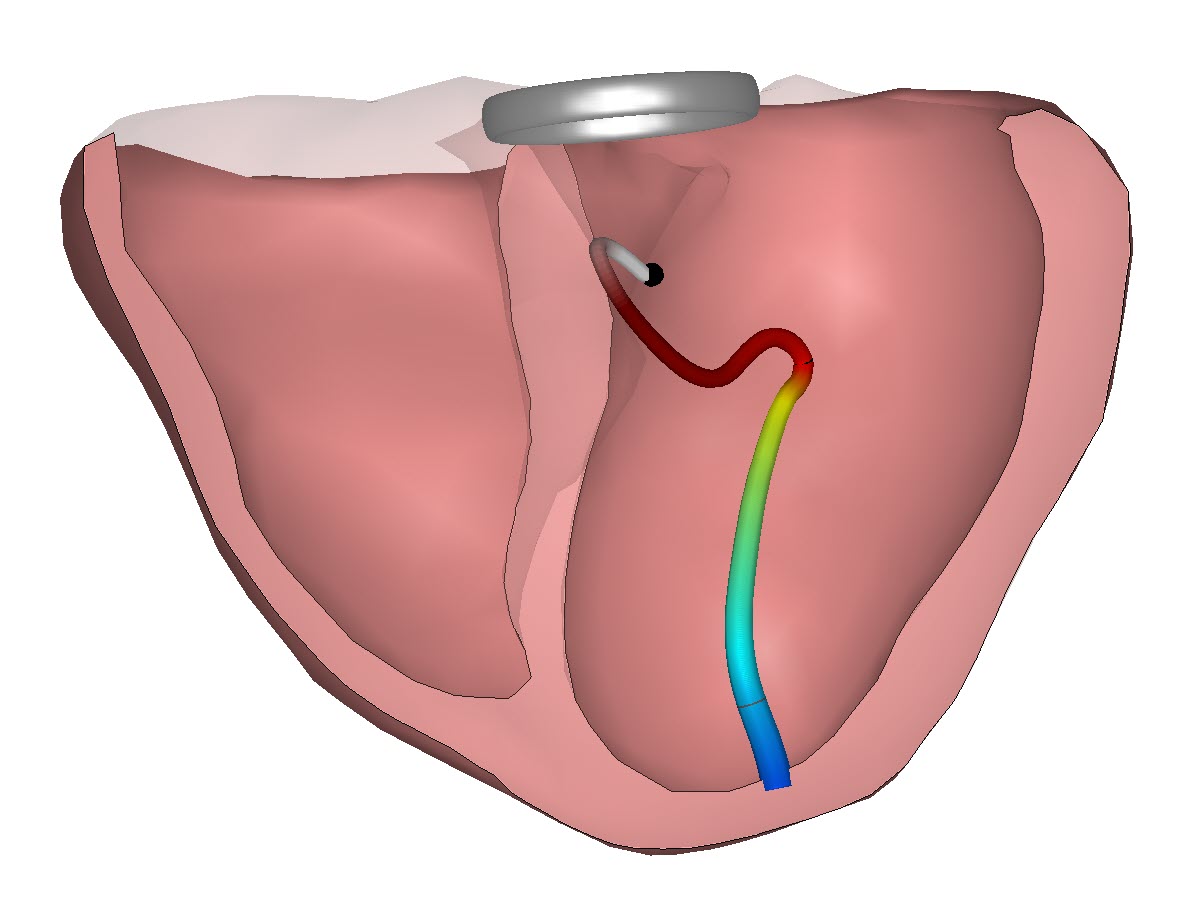
As a team focused on obtaining more information from the 12 lead Electrocardiogram we know there’s more to see in the ECG. And addressing the challenge of detecting ischemia without arteries obstruction is one of the R&D focal points in our activities. We already know that our approach which links the ECG data to the heart anatomy is effective in identifying conduction tissue changes due to Ischemia. And we have embarked on a joint project with the University of Utrecht to learn more on the options of using ECG markers for early detection. This blog will periodically report on the progress in this research.