Occasionally we use this blog to present CineECG applied to detect more complex disorders, in this case a complex progressive conduction block. The complexity of this case is due to the two level AV-junctional conduction block, resulting in group beating bradycardia with the combination of a right bundle branch (RBB) and a left anterior fascicle (LAF) Wenckebach block combined with a Mobitz II block of the left posterior fascicle (LPF).
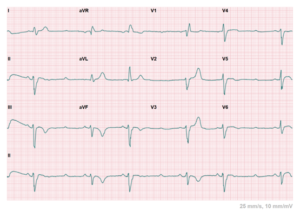
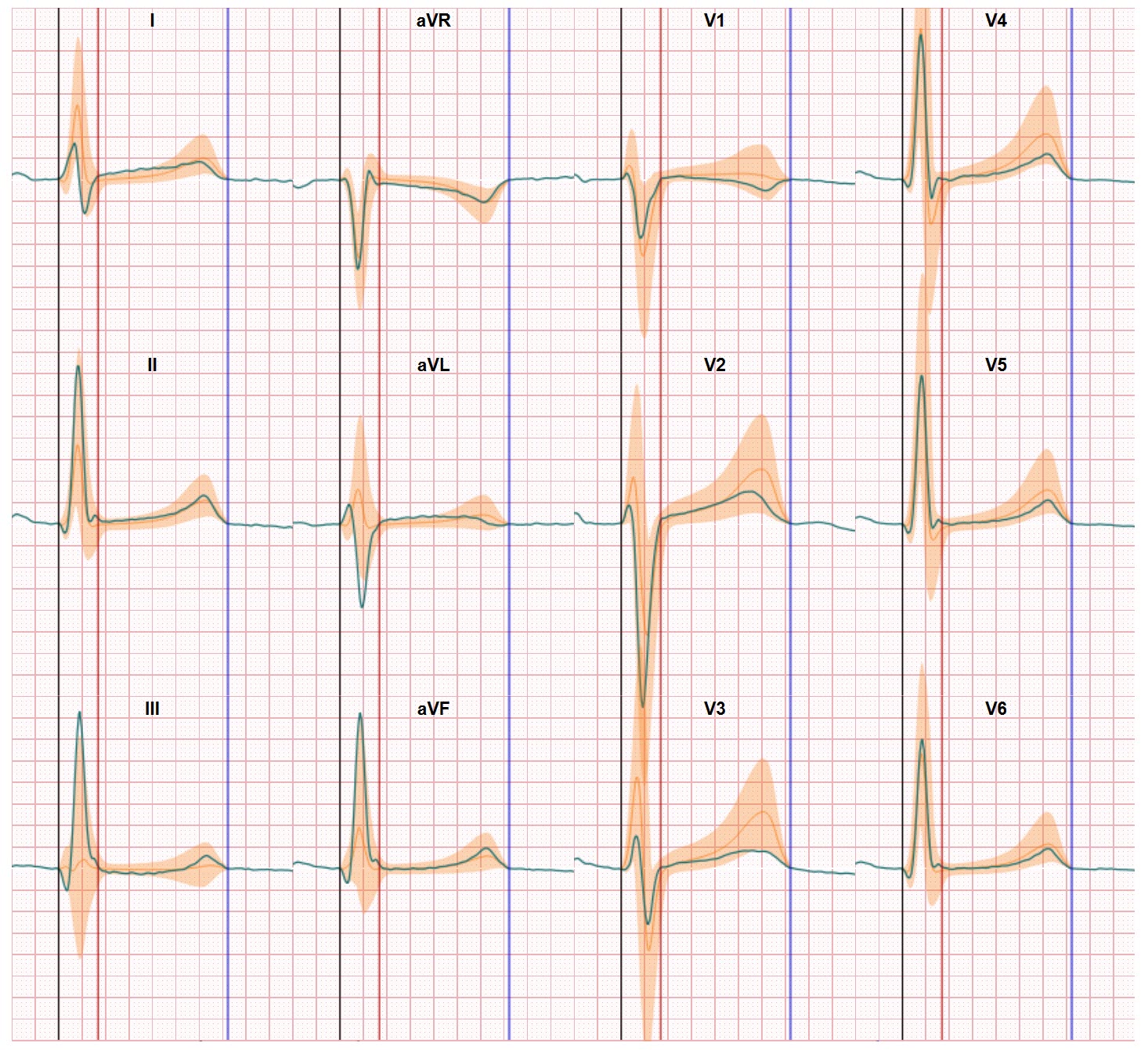
The ECG displays a sequence of five P waves: the second and fourth P wave are blocked proximally in the His-Purkinje system, the first P wave is conducted with RBB aberrancy and incomplete LAF aberrancy, the third one with complete RBBB and left anterior fascicular block (LAFB), and the fifth P wave is followed by complete fascicular block. And a Wenckebach sequence, concealed in the RBB and overt in the LAF leads to the different QRS configurations in subsequent beats.
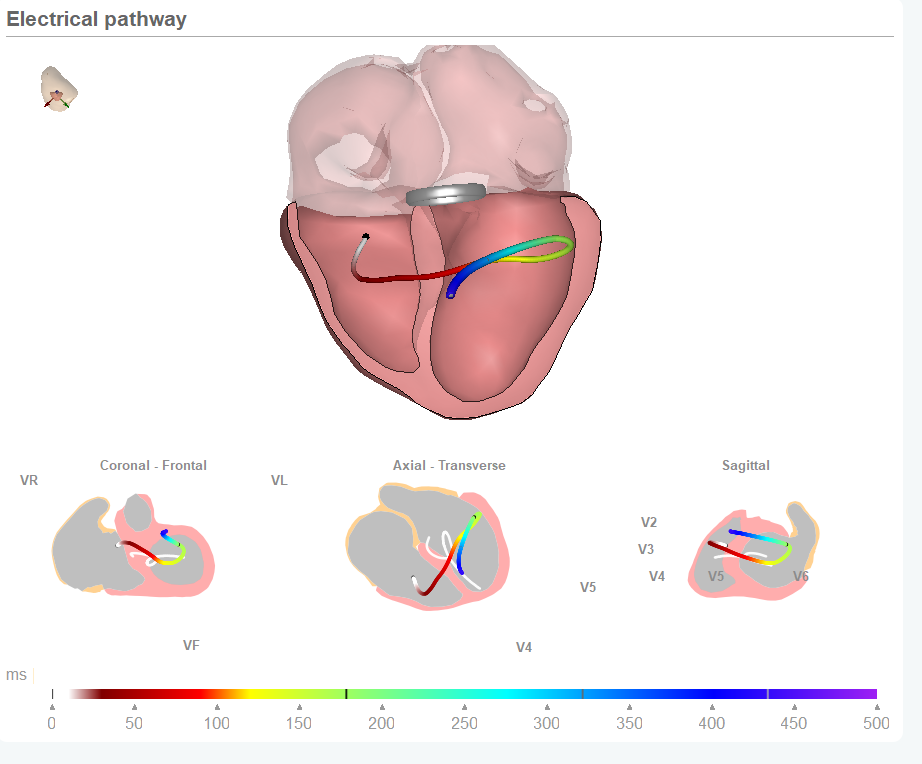
Applying CineECG on different beats supports the identification of the differences in conduction disorders. Because CineECG relates the ECG data to the heart anatomy it visualizes the different averaged activation pathways.
First CineECG (first beat)
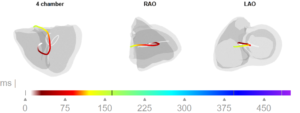
In the first CineECG graphic we see the average electrical pathway resulting from the first beat. Similar to the normal CineECG, the initiation site is located close to the septum and initially moves from the left towards the right ventricle. It then moves towards inferior and subsequently far back to superior, clearly demonstrating an abnormal abnormal activation pattern.
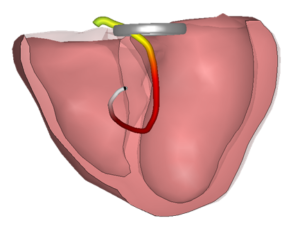
The late activation to the right is in the complete opposite direction as expected in the normal CineECG.
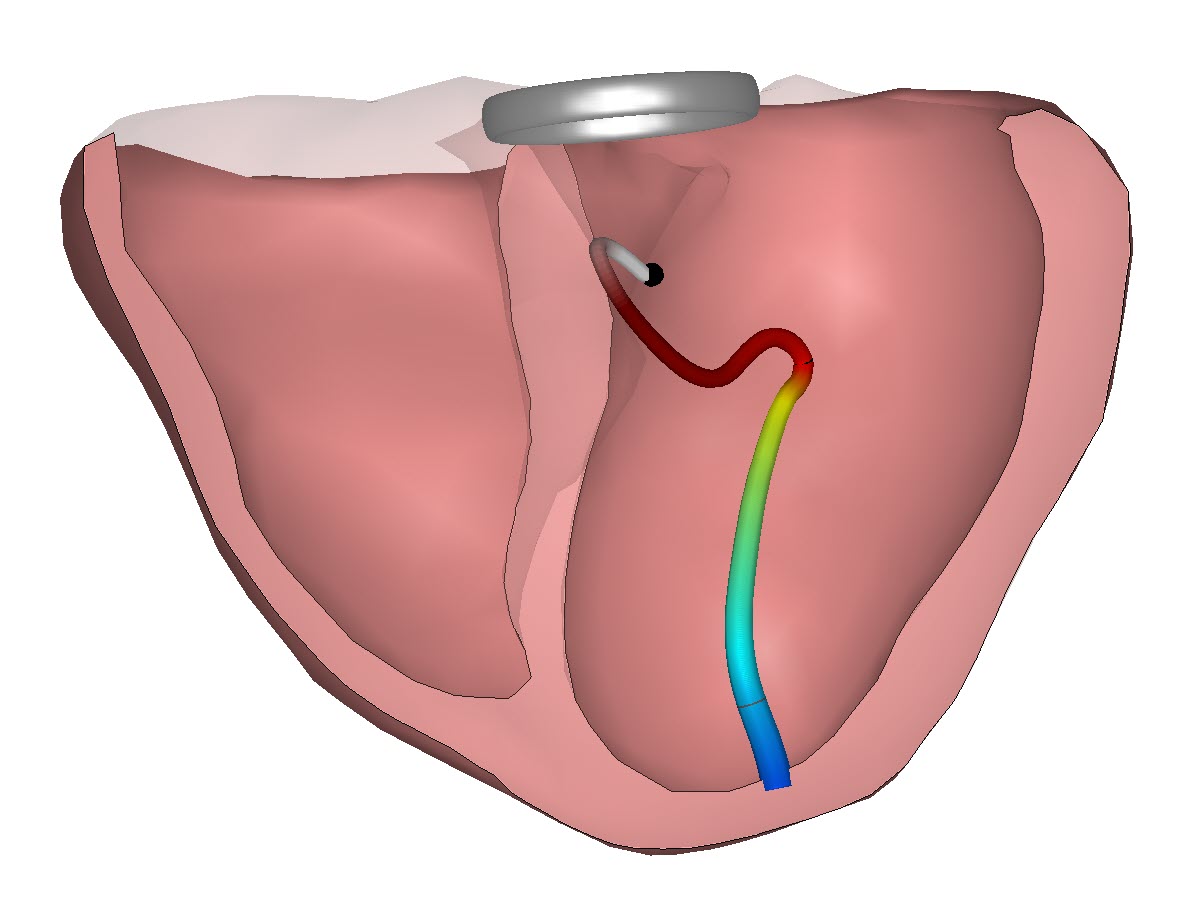
Second CineECG (third beat)
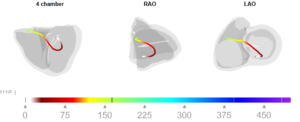
The CineECG of the QRS complex after the third P wave is presented in the next graph. The beginning of the CineECG trajectory is positioned far to the left, on the posterior left ventricular wall.
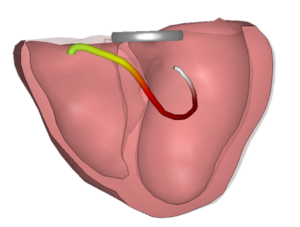
It then moves to inferior, after which the most part of the trajectory is directed completely towards the right ventricle, also showing a prolonged trajectory. This CineECG shows very little similarities to a normal CineECG trajectory, indicating completely abnormal ventricular activation.
Article in Journal of Electrocardiology
There’s much more detail available regarding this complex progressive conduction block case and if you want to learn more you can read the full case study in the recent edition of the Journal of Electrocardiology.
This case study has been written down by Iris van der Schaaf and Ton Gorgels and they have done a great job. If you want to learn more on how CineECG can help you as a medical professional in ECG interpretation you can find more information on the CineECG website.